A little context
When it comes to Climate, Community and Biodiversity (CCB), It is important understand that this standard belongs to one of many standards that are found in the Voluntary carbon Standard.
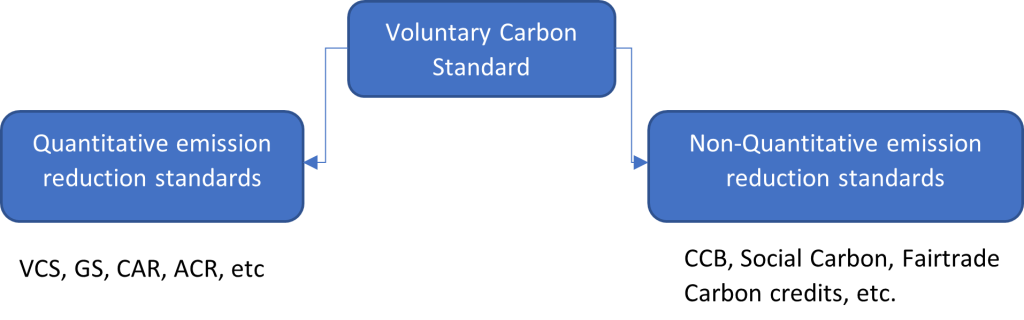
Inside of the Voluntary carbon standard there are two types of certificates. On the one hand, those that quantify the reduction of emissions by companies. That is, they have standardized methods to determine the reduction of carbon emissions achieved from a carbon credit project. Some examples of these standards are VCS, Gold Standard, American Carbon Registry, Climate Action Reserve, etc.
On the other hand, there are others that do not issue emission reduction certificates but are designed to complement the previous certifications. The latter, called “non-quantitative standards”, seek to evaluate the social, environmental and economic impact of each carbon credit project (called “co-benefits”). Non-quantitative standards are used to assess and communicate the co-benefits of carbon offset projects.
What is the Climate, Community and Biodiversity (CCB) standard?
The Climate, Community, and Biodiversity Standards (CCB Standards) are a set of guidelines and criteria for evaluating the environmental and social impacts of climate change mitigation projects. These standards provide a framework for assessing the effectiveness of projects in achieving their intended goals while also ensuring that they do not harm local communities or biodiversity.
The CCB Standards were developed by a group of environmental and social organizations, including the Rainforest Alliance, the Wildlife Conservation Society, and the Climate, Community & Biodiversity Alliance. These organizations recognized the need for a comprehensive set of standards to ensure that climate change mitigation projects were not causing unintended harm to local communities or the environment.
Climate, Community and Biodiversity (CCB) standards are often used in conjunction with other quantitative standards such as VCS or Gold Standard. The CCB Standards are built on three core principles:
- Climate Change Mitigation (refers to projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions or increase carbon sequestration)
- Community benefits (refer to projects that provide economic, social, or cultural benefits to local communities, such as job creation, improved infrastructure, or access to clean water)
- Biodiversity Conservation (refers to projects that protect or enhance the biodiversity of ecosystems and species)
There are currently close to 200 projects validated under CCB standards. These cover around 10 million hectares around the world.

How to apply to the CCB (Climate, Community and Biodiversity) standard?
To be certified under the CCB Standards, projects must meet specific criteria under each of these three principles. For example, to meet the climate change mitigation criteria, a project must demonstrate that it is reducing greenhouse gas emissions or increasing carbon sequestration beyond business-as-usual scenarios. To meet the community benefits criteria, a project must demonstrate that it is providing tangible benefits to local communities, such as employment opportunities or improved access to healthcare. To meet the biodiversity conservation criteria, a project must demonstrate that it is protecting or enhancing the biodiversity of ecosystems and species in the project area.
The CCB Standards also include requirements for monitoring and reporting on project performance over time. Projects must regularly report on their greenhouse gas emissions reductions or carbon sequestration, as well as their impacts on local communities and biodiversity. This monitoring and reporting helps ensure that projects remain in compliance with the CCB Standards and that they are meeting their intended goals.

Certification under the CCB Standards is voluntary but can provide several benefits to projects. Certified projects can access new sources of funding, as some investors require CCB certification as a condition for funding. Additionally, certification can enhance a project’s credibility and reputation, as it demonstrates a commitment to environmental and social responsibility.
Conclusion
In summary, the Climate Change and Biodiversity Community (CCB) is an international organization dedicated to promoting biodiversity conservation and climate change mitigation. CCB works with a wide range of members to develop rigorous standards and certifications for biodiversity conservation and GHG emission reduction projects, and also promotes education and public awareness. CCB believes that addressing climate change and biodiversity loss is essential to ensure a sustainable future for our planet and its inhabitants.
At ALLCOT Trading, our mission is to promote additional sustainable impact with every transaction. If you want to achieve this in a fair, transparent and win-win scenario, contact us and together we will make it happen.



